Cyproterone Acetate on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Cyproterone acetate (CPA), sold alone under the brand name Androcur or with ethinylestradiol under the brand names Diane or Diane-35 among others, is an
 The dehydrogenation of 17α-hydroxyprogesterone acetate 02-23-8(1) with chloranil (tetrachloro-p-benzoquinone) gives a compound that has been called melengestro acetate 25-51-4(2). Dehydrogenation with selenium dioxide gives 17-acetoxy-1,4,6-pregnatriene-3,20-dione 668-75-9(3). Reacting this with diazomethane results in a 1,3-dipolar addition reaction at C1–C2 of the double bond of the steroid system, which forms a derivative of dihydropyrazole
The dehydrogenation of 17α-hydroxyprogesterone acetate 02-23-8(1) with chloranil (tetrachloro-p-benzoquinone) gives a compound that has been called melengestro acetate 25-51-4(2). Dehydrogenation with selenium dioxide gives 17-acetoxy-1,4,6-pregnatriene-3,20-dione 668-75-9(3). Reacting this with diazomethane results in a 1,3-dipolar addition reaction at C1–C2 of the double bond of the steroid system, which forms a derivative of dihydropyrazole
CID:134990386
(4). This compound cleaves when reacted with
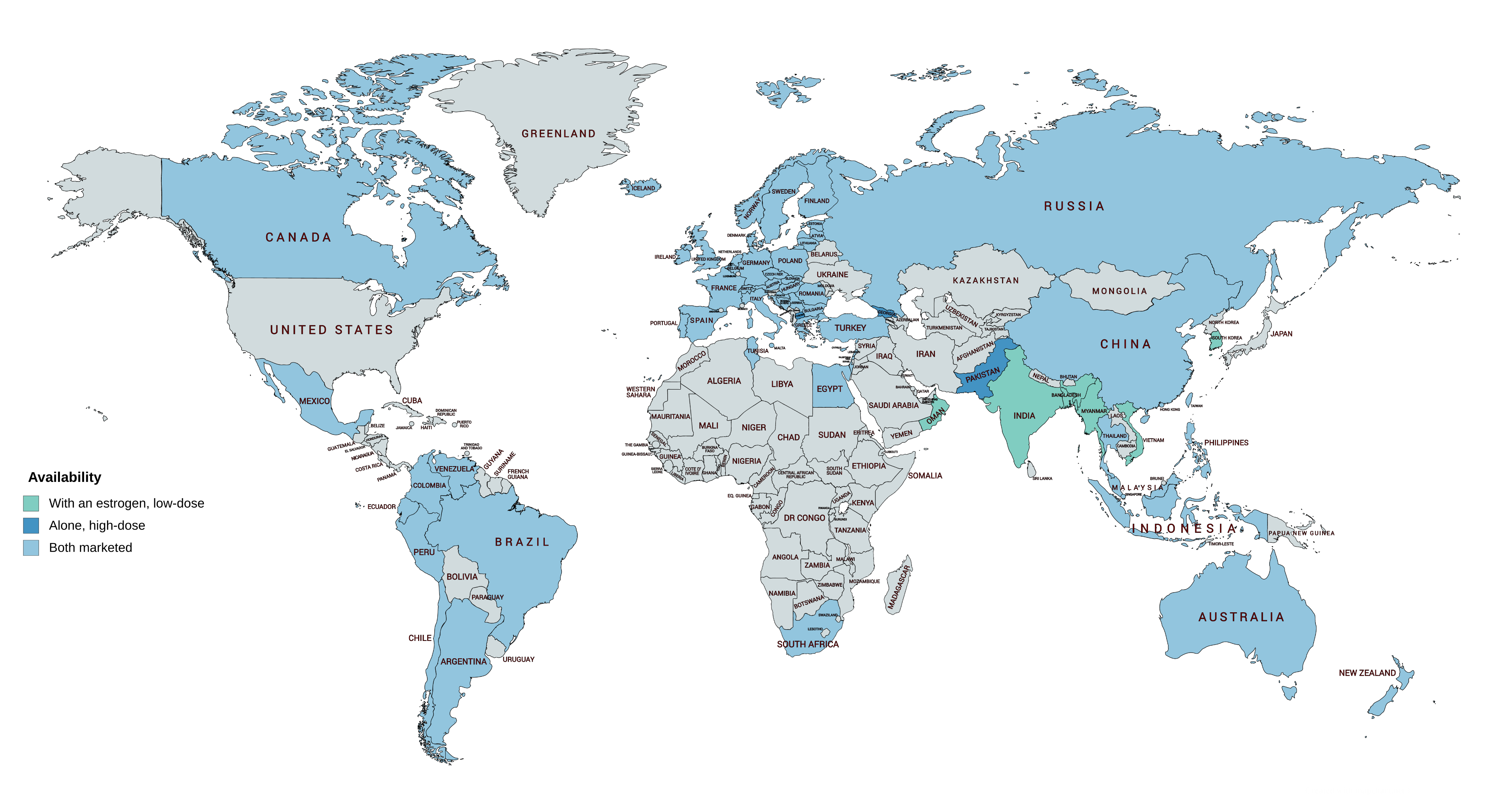 CPA is widely available throughout the world, and is marketed in almost every developed country, with the notable major exceptions of the
CPA is widely available throughout the world, and is marketed in almost every developed country, with the notable major exceptions of the
Die Geschichte des Wirkstoffs Cyproteronazetat: Von der "Pille für den Mann" zum "Hautpflegemittel mit Empfängnisschutz" [The History of Cyproterone Acetate: From the "Pill for Men" to the "Skin Care Product and Contraceptive"
/nowiki> - Arznei-Telegramm]
[ Google_Translate
/nowiki>.html" ;"title="/nowiki>Google Translate"> /nowiki>Google_Translate">[ Google_Translate
/nowiki> {{Navboxes .html" ;"title="/nowiki>Google Translate
/nowiki>">/nowiki>Google Translate">[ Google Translate
/nowiki> {{Navboxes "> title = Pharmacodynamics , titlestyle = background:#ccccff , list1 = {{Androgen receptor modulators {{Aryl hydrocarbon receptor modulators {{Glucocorticoid receptor modulators {{Opioid receptor modulators {{Progesterone receptor modulators {{Xenobiotic-sensing receptor modulators Cyproterone acetate, 3β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase inhibitors Acetate esters Anti-acne preparations Antiandrogen esters Antigonadotropins Aryl hydrocarbon receptor antagonists Chloroarenes Cyclopropanes CYP17A1 inhibitors Enones Glucocorticoids Hair loss medications Hair removal Hepatotoxins Hormonal antineoplastic drugs Ketones Pregnane X receptor agonists Pregnanes Progestogen esters Progestogens Prolactin releasers Prostate cancer Steroidal antiandrogens
antiandrogen
Antiandrogens, also known as androgen antagonists or testosterone blockers, are a class of drugs that prevent androgens like testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT) from mediating their biological effects in the body. They act by blocking the ...
and progestin
A progestogen, also referred to as a progestagen, gestagen, or gestogen, is a type of medication which produces effects similar to those of the natural female sex hormone progesterone in the body. A progestin is a ''synthetic'' progestogen. Pro ...
medication used in the treatment of androgen-dependent conditions such as acne
Acne, also known as ''acne vulgaris'', is a long-term skin condition that occurs when dead skin cells and oil from the skin clog hair follicles. Typical features of the condition include blackheads or whiteheads, pimples, oily skin, and ...
, excessive body hair growth, early puberty, and prostate cancer
Prostate cancer is cancer of the prostate. Prostate cancer is the second most common cancerous tumor worldwide and is the fifth leading cause of cancer-related mortality among men. The prostate is a gland in the male reproductive system that su ...
, as a component of feminizing hormone therapy
Feminizing hormone therapy, also known as transfeminine hormone therapy, is hormone therapy and sex reassignment therapy to change the secondary sex characteristics of transgender people from masculine or androgynous to feminine. It is a co ...
for transgender women
A trans woman or a transgender woman is a woman who was assigned male at birth. Trans women have a female gender identity, may experience gender dysphoria, and may transition; this process commonly includes hormone replacement therapy and so ...
, and in birth control pill
The combined oral contraceptive pill (COCP), often referred to as the birth control pill or colloquially as "the pill", is a type of birth control that is designed to be taken orally by women. The pill contains two important hormones: progesti ...
s. It is formulated and used both alone and in combination with an estrogen
Estrogen or oestrogen is a category of sex hormone responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics. There are three major endogenous estrogens that have estrogenic hormonal ac ...
. CPA is taken by mouth
Oral administration is a route of administration where a substance is taken through the mouth. Per os abbreviated to P.O. is sometimes used as a direction for medication to be taken orally. Many medications are taken orally because they are i ...
one to three times per day.
Common side effect
In medicine, a side effect is an effect, whether therapeutic or adverse, that is secondary to the one intended; although the term is predominantly employed to describe adverse effects, it can also apply to beneficial, but unintended, consequence ...
s of high-dose CPA in men include gynecomastia
Gynecomastia (also spelled gynaecomastia) is the abnormal non-cancerous enlargement of one or both breasts in males due to the growth of breast tissue as a result of a hormone imbalance between estrogens and androgens. Updated by Brent Wisse ( ...
(breast development) and feminization. In both men and women, possible side effects of CPA include low sex hormone levels, reversible infertility
Infertility is the inability of a person, animal or plant to reproduce by natural means. It is usually not the natural state of a healthy adult, except notably among certain eusocial species (mostly haplodiploid insects). It is the normal st ...
, sexual dysfunction
Sexual dysfunction is difficulty experienced by an individual or partners during any stage of normal sexual activity, including physical pleasure, desire, preference, arousal, or orgasm. The World Health Organization defines sexual dysfunction a ...
, fatigue
Fatigue describes a state of tiredness that does not resolve with rest or sleep. In general usage, fatigue is synonymous with extreme tiredness or exhaustion that normally follows prolonged physical or mental activity. When it does not resolve ...
, depression, weight gain
Weight gain is an increase in body weight. This can involve an increase in muscle mass, fat deposits, excess fluids such as water or other factors. Weight gain can be a symptom of a serious medical condition.
Description
Weight gain occurs w ...
, and elevated liver enzymes
In medicine, the presence of elevated transaminases, commonly the transaminases alanine transaminase (ALT) and aspartate transaminase (AST), may be an indicator of liver dysfunction. Other terms include transaminasemia, transaminitis, and elevated ...
. At very high doses in older individuals, significant cardiovascular
The blood circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the entire body of a human or other vertebrate. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, tha ...
complications can occur. Rare but serious adverse reactions of CPA include blood clot
A thrombus (plural thrombi), colloquially called a blood clot, is the final product of the blood coagulation step in hemostasis. There are two components to a thrombus: aggregated platelets and red blood cells that form a plug, and a mesh of cr ...
s, liver damage
Liver disease, or hepatic disease, is any of many diseases of the liver. If long-lasting it is termed chronic liver disease. Although the diseases differ in detail, liver diseases often have features in common.
Signs and symptoms
Some of the si ...
and brain tumor
A brain tumor occurs when abnormal cells form within the brain. There are two main types of tumors: malignant tumors and benign (non-cancerous) tumors. These can be further classified as primary tumors, which start within the brain, and seco ...
s. CPA can also cause adrenal insufficiency
Adrenal insufficiency is a condition in which the adrenal glands do not produce adequate amounts of steroid hormones. The adrenal gland normally secretes glucocorticoids (primarily cortisol), mineralocorticoids (primarily aldosterone), and andro ...
as a withdrawal effect if it is discontinued abruptly from a high dosage. CPA blocks the effects of androgen
An androgen (from Greek ''andr-'', the stem of the word meaning "man") is any natural or synthetic steroid hormone that regulates the development and maintenance of male characteristics in vertebrates by binding to androgen receptors. This in ...
s such as testosterone
Testosterone is the primary sex hormone and anabolic steroid in males. In humans, testosterone plays a key role in the development of male reproductive tissues such as testes and prostate, as well as promoting secondary sexual characteristi ...
in the body, which it does by preventing them from interacting with their biological target
A biological target is anything within a living organism to which some other entity (like an endogenous ligand or a drug) is directed and/or binds, resulting in a change in its behavior or function. Examples of common classes of biological targets ...
, the androgen receptor
The androgen receptor (AR), also known as NR3C4 (nuclear receptor subfamily 3, group C, member 4), is a type of nuclear receptor that is activated by binding any of the androgenic hormones, including testosterone and dihydrotestosterone in ...
(AR), and by reducing their production by the gonad
A gonad, sex gland, or reproductive gland is a mixed gland that produces the gametes and sex hormones of an organism. Female reproductive cells are egg cells, and male reproductive cells are sperm. The male gonad, the testicle, produces sp ...
s, hence their concentrations in the body. In addition, it has progesterone
Progesterone (P4) is an endogenous steroid and progestogen sex hormone involved in the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, and embryogenesis of humans and other species. It belongs to a group of steroid hormones called the progestogens and is the majo ...
-like effects by activating the progesterone receptor
The progesterone receptor (PR), also known as NR3C3 or nuclear receptor subfamily 3, group C, member 3, is a protein found inside cells. It is activated by the steroid hormone progesterone.
In humans, PR is encoded by a single ''PGR'' gene resid ...
(PR). It can also produce weak cortisol
Cortisol is a steroid hormone, in the glucocorticoid class of hormones. When used as a medication, it is known as hydrocortisone.
It is produced in many animals, mainly by the '' zona fasciculata'' of the adrenal cortex in the adrenal g ...
-like effects at very high doses.
CPA was discovered in 1961. It was originally developed as a progestin. In 1965, the antiandrogenic effects of CPA were discovered. CPA was first marketed, as an antiandrogen, in 1973, and was the first antiandrogen to be introduced for medical use. A few years later, in 1978, CPA was introduced as a progestin in a birth control pill. It has been described as a "first-generation" progestin and as the prototypical antiandrogen. CPA is available widely throughout the world. An exception is the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
, where it is not approved for use.
Medical uses
CPA is used as aprogestin
A progestogen, also referred to as a progestagen, gestagen, or gestogen, is a type of medication which produces effects similar to those of the natural female sex hormone progesterone in the body. A progestin is a ''synthetic'' progestogen. Pro ...
and antiandrogen
Antiandrogens, also known as androgen antagonists or testosterone blockers, are a class of drugs that prevent androgens like testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT) from mediating their biological effects in the body. They act by blocking the ...
in hormonal birth control
Hormonal contraception refers to birth control methods that act on the endocrine system. Almost all methods are composed of steroid hormones, although in India one selective estrogen receptor modulator is marketed as a contraceptive. The origina ...
and in the treatment of androgen-dependent conditions. Specifically, CPA is used in combined birth control pill
The combined oral contraceptive pill (COCP), often referred to as the birth control pill or colloquially as "the pill", is a type of birth control that is designed to be taken orally by women. The pill contains two important hormones: progesti ...
s, in the treatment of androgen-dependent skin and hair conditions such as acne
Acne, also known as ''acne vulgaris'', is a long-term skin condition that occurs when dead skin cells and oil from the skin clog hair follicles. Typical features of the condition include blackheads or whiteheads, pimples, oily skin, and ...
, seborrhea, excessive hair growth, and scalp hair loss
Pattern hair loss (also known as androgenetic alopecia (AGA)) is a hair loss condition that primarily affects the top and front of the scalp. In male-pattern hair loss (MPHL), the hair loss typically presents itself as either a receding front ...
, high androgen levels, in transgender hormone therapy
Transgender hormone therapy, also called hormone replacement therapy (HRT) or gender-affirming hormone therapy (GAHT), is a form of hormone therapy in which sex hormones and other hormonal medications are administered to transgender or gender non ...
, to treat prostate cancer
Prostate cancer is cancer of the prostate. Prostate cancer is the second most common cancerous tumor worldwide and is the fifth leading cause of cancer-related mortality among men. The prostate is a gland in the male reproductive system that su ...
, to reduce sex drive in sex offender
A sex offender (sexual offender, sex abuser, or sexual abuser) is a person who has committed a sex crime. What constitutes a sex crime differs by culture and legal jurisdiction. The majority of convicted sex offenders have convictions for crim ...
s or men with paraphilia
Paraphilia (previously known as sexual perversion and sexual deviation) is the experience of intense sexual arousal to atypical objects, situations, fantasies, behaviors, or individuals. It has also been defined as sexual interest in anything ot ...
s or hypersexuality, to treat early puberty, and for other uses. It is used both at low doses and at higher doses.
In the United States, where CPA is not available, other medications with antiandrogenic effects are used to treat androgen-dependent conditions instead. Examples of such medications include gonadotropin-releasing hormone modulators (GnRH modulators) like leuprorelin
Leuprorelin, also known as leuprolide, is a manufactured version of a hormone used to treat prostate cancer, breast cancer, endometriosis, uterine fibroids, as part of transgender hormone therapy, for early puberty, or to perform chemical c ...
and degarelix
Degarelix, sold under the brand name Firmagon among others, is a hormonal therapy used in the treatment of prostate cancer.
Testosterone is a male hormone that promotes growth of many prostate tumours and therefore reducing circulating testost ...
, nonsteroidal antiandrogens like flutamide and bicalutamide, the diuretic
A diuretic () is any substance that promotes diuresis, the increased production of urine. This includes forced diuresis. A diuretic tablet is sometimes colloquially called a water tablet. There are several categories of diuretics. All diuretics i ...
and steroidal antiandrogen spironolactone
Spironolactone, sold under the brand name Aldactone among others, is a medication that is primarily used to treat fluid build-up due to heart failure, liver scarring, or kidney disease. It is also used in the treatment of high blood press ...
, the progestin
A progestogen, also referred to as a progestagen, gestagen, or gestogen, is a type of medication which produces effects similar to those of the natural female sex hormone progesterone in the body. A progestin is a ''synthetic'' progestogen. Pro ...
medroxyprogesterone acetate
Medroxyprogesterone acetate (MPA), also known as depot medroxyprogesterone acetate (DMPA) in injectable form and sold under the brand name Depo-Provera among others, is a hormonal medication of the progestin type. It is used as a method of bi ...
, and the 5α-reductase inhibitor
5α-Reductases, also known as 3-oxo-5α-steroid 4-dehydrogenases, are enzymes involved in steroid metabolism. They participate in three metabolic pathways: bile acid biosynthesis, androgen and estrogen metabolism. There are three isozymes o ...
s finasteride
Finasteride, sold under the brand names Proscar and Propecia among others, is a medication used to treat hair loss and benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) in men. It can also be used to treat excessive hair growth in women and as a part of h ...
and dutasteride. The steroidal antiandrogen and progestin chlormadinone acetate is used as an alternative to CPA in Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the n ...
, South Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia, constituting the southern part of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and sharing a Korean Demilitarized Zone, land border with North Korea. Its western border is formed ...
, and a few other countries.
Birth control
CPA is used withethinylestradiol
Ethinylestradiol (EE) is an estrogen medication which is used widely in birth control pills in combination with progestins. In the past, EE was widely used for various indications such as the treatment of menopausal symptoms, gynecological disord ...
as a combined birth control pill
The combined oral contraceptive pill (COCP), often referred to as the birth control pill or colloquially as "the pill", is a type of birth control that is designed to be taken orally by women. The pill contains two important hormones: progesti ...
to prevent pregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring develops ( gestates) inside a woman's uterus (womb). A multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Pregnancy usually occurs by sexual intercourse, but ...
. This birth control combination has been available since 1978. The formulation is taken once daily for 21 days, followed by a 7-day free interval.https://www.bayer.ca/omr/online/diane-35-pm-en.pdf CPA has also been available in combination with estradiol valerate (brand name Femilar) as a combined birth control pill in Finland
Finland ( fi, Suomi ; sv, Finland ), officially the Republic of Finland (; ), is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It shares land borders with Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of Bot ...
since 1993. High-dose CPA tablets have a contraceptive effect and can be used as a form of birth control, although they are not specifically licensed as such.
Skin and hair conditions
Females
CPA is used as an antiandrogen to treat androgen-dependent skin and hair conditions such asacne
Acne, also known as ''acne vulgaris'', is a long-term skin condition that occurs when dead skin cells and oil from the skin clog hair follicles. Typical features of the condition include blackheads or whiteheads, pimples, oily skin, and ...
, seborrhea, hirsutism (excessive hair growth), scalp hair loss
Pattern hair loss (also known as androgenetic alopecia (AGA)) is a hair loss condition that primarily affects the top and front of the scalp. In male-pattern hair loss (MPHL), the hair loss typically presents itself as either a receding front ...
, and hidradenitis suppurativa
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS), sometimes known as acne inversa or Verneuil's disease, is a long-term dermatological condition characterized by the occurrence of inflamed and swollen lumps. These are typically painful and break open, releasin ...
in women. These conditions are worsened by the presence of androgens, and by suppressing androgen levels and blocking their actions, CPA improves the symptoms of these conditions. CPA is used to treat such conditions both at low doses as a birth control pill and on its own at higher doses. A birth control pill containing low-dose CPA in combination with ethinylestradiol
Ethinylestradiol (EE) is an estrogen medication which is used widely in birth control pills in combination with progestins. In the past, EE was widely used for various indications such as the treatment of menopausal symptoms, gynecological disord ...
to treat acne has been found to result in overall improvement in 75 to 90% of women, with responses approaching 100% improvement. High-dose CPA alone likewise has been found to improve symptoms of acne by 75 to 90% in women. Discontinuation of CPA has been found to result in marked recurrence of symptoms in up to 70% of women. CPA is one of the most commonly used medications in the treatment of hirsutism, hyperandrogenism, and polycystic ovary syndrome in women throughout the world.
Higher dosages of CPA are used in combination with an estrogen specifically at doses of 25 to 100 mg/day cyclically in the treatment of hirsutism in women. The efficacy of such dosages of CPA in the treatment of hirsutism in women appear to be similar to that of spironolactone
Spironolactone, sold under the brand name Aldactone among others, is a medication that is primarily used to treat fluid build-up due to heart failure, liver scarring, or kidney disease. It is also used in the treatment of high blood press ...
, flutamide, and finasteride
Finasteride, sold under the brand names Proscar and Propecia among others, is a medication used to treat hair loss and benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) in men. It can also be used to treat excessive hair growth in women and as a part of h ...
. Randomized controlled trial
A randomized controlled trial (or randomized control trial; RCT) is a form of scientific experiment used to control factors not under direct experimental control. Examples of RCTs are clinical trials that compare the effects of drugs, surgical t ...
s have found that higher dosages of CPA (e.g., 20 mg/day or 100 mg/day) added cyclically to a birth control pill
The combined oral contraceptive pill (COCP), often referred to as the birth control pill or colloquially as "the pill", is a type of birth control that is designed to be taken orally by women. The pill contains two important hormones: progesti ...
containing ethinylestradiol
Ethinylestradiol (EE) is an estrogen medication which is used widely in birth control pills in combination with progestins. In the past, EE was widely used for various indications such as the treatment of menopausal symptoms, gynecological disord ...
and 2 mg/day CPA were no more effective or only marginally more effective in the treatment of severe hirsutism in women than the birth control pill alone. Maintenance therapy with lower doses of CPA, such as 25 mg/day, has been found to be effective in preventing relapse of symptoms of hirsutism. CPA has typically been combined with ethinylestradiol, but it can alternatively be used in combination with hormone replacement therapy
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT), also known as menopausal hormone therapy or postmenopausal hormone therapy, is a form of hormone therapy used to treat symptoms associated with female menopause. These symptoms can include hot flashes, vaginal ...
dosages of estradiol
Estradiol (E2), also spelled oestradiol, is an estrogen steroid hormone and the major female sex hormone. It is involved in the regulation of the estrous and menstrual female reproductive cycles. Estradiol is responsible for the development o ...
instead. CPA at a dosage of 50 mg/day in combination with 100 μg/day transdermal estradiol patches has been found to be effective in the treatment of hirsutism similarly to the combination of CPA with ethinylestradiol.
The efficacy of the combination of an estrogen and CPA in the treatment of hirsutism in women appears to be due to marked suppression of total and free androgen
An androgen (from Greek ''andr-'', the stem of the word meaning "man") is any natural or synthetic steroid hormone that regulates the development and maintenance of male characteristics in vertebrates by binding to androgen receptors. This in ...
levels as well as additional blockade of the androgen receptor
The androgen receptor (AR), also known as NR3C4 (nuclear receptor subfamily 3, group C, member 4), is a type of nuclear receptor that is activated by binding any of the androgenic hormones, including testosterone and dihydrotestosterone in ...
.
Males
CPA has been found to be effective in the treatment of acne in males, with marked improvement in symptoms observed at dosages of 25, 50, and 100 mg/day in different studies. It can also halt further progression of scalp hair loss in men. Increased head hair and decreased body hair has been observed with CPA in men with scalp hair loss. However, its side effects in men, such asdemasculinization
Virilization or masculinization is the biological development of adult male characteristics in young males or females. Most of the changes of virilization are produced by androgens.
Virilization is most commonly used in three medical and biology ...
, gynecomastia
Gynecomastia (also spelled gynaecomastia) is the abnormal non-cancerous enlargement of one or both breasts in males due to the growth of breast tissue as a result of a hormone imbalance between estrogens and androgens. Updated by Brent Wisse ( ...
, sexual dysfunction
Sexual dysfunction is difficulty experienced by an individual or partners during any stage of normal sexual activity, including physical pleasure, desire, preference, arousal, or orgasm. The World Health Organization defines sexual dysfunction a ...
, bone density
Bone density, or bone mineral density, is the amount of bone mineral in bone tissue. The concept is of mass of mineral per volume of bone (relating to density in the physics sense), although clinically it is measured by proxy according to optic ...
loss, and reversible infertility
Infertility is the inability of a person, animal or plant to reproduce by natural means. It is usually not the natural state of a healthy adult, except notably among certain eusocial species (mostly haplodiploid insects). It is the normal st ...
, make the use of CPA in males impractical in most cases. In addition, lower dosages of CPA, such as 25 mg/day, have been found to be better-tolerated in men. But such doses also show lower effectiveness in the treatment of acne in men.
High androgen levels
CPA is used as an antiandrogen to treat high androgen levels and associatedsymptom
Signs and symptoms are the observed or detectable signs, and experienced symptoms of an illness, injury, or condition. A sign for example may be a higher or lower temperature than normal, raised or lowered blood pressure or an abnormality showi ...
s such as masculinization
Virilization or masculinization is the biological development of adult male characteristics in young males or females. Most of the changes of virilization are produced by androgens.
Virilization is most commonly used in three medical and biology ...
due to conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome
Polycystic ovary syndrome, or PCOS, is the most common endocrine disorder in women of reproductive age. The syndrome is named after the characteristic cysts which may form on the ovaries, though it is important to note that this is a sign and no ...
(PCOS) and congenital adrenal hyperplasia
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) is a group of autosomal recessive disorders characterized by impaired cortisol synthesis. It results from the deficiency of one of the five enzymes required for the synthesis of cortisol in the adrenal cortex ...
(CAH) in women. It is almost always combined with an estrogen, such as ethinylestradiol
Ethinylestradiol (EE) is an estrogen medication which is used widely in birth control pills in combination with progestins. In the past, EE was widely used for various indications such as the treatment of menopausal symptoms, gynecological disord ...
, when it is used in the treatment of PCOS in women.
Menopausal hormone therapy
CPA is used at low doses in menopausal hormone therapy in combination with an estrogen to provide endometrial protection and treat menopausal symptoms. It is used in menopausal hormone therapy under the brand name Climen, which is a sequential preparation that contains 2 mg estradiol valerate and 1 mg CPA. Climen was the first product for use in menopausal hormone therapy containing CPA to be marketed. It is available in more than 40 countries.Transgender hormone therapy
CPA is widely used as anantiandrogen
Antiandrogens, also known as androgen antagonists or testosterone blockers, are a class of drugs that prevent androgens like testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT) from mediating their biological effects in the body. They act by blocking the ...
and progestogen
Progestogens, also sometimes written progestagens or gestagens, are a class of natural or synthetic steroid hormones that bind to and activate the progesterone receptors (PR). Progesterone is the major and most important progestogen in the bod ...
in feminizing hormone therapy
Feminizing hormone therapy, also known as transfeminine hormone therapy, is hormone therapy and sex reassignment therapy to change the secondary sex characteristics of transgender people from masculine or androgynous to feminine. It is a co ...
for transgender women
A trans woman or a transgender woman is a woman who was assigned male at birth. Trans women have a female gender identity, may experience gender dysphoria, and may transition; this process commonly includes hormone replacement therapy and so ...
. It is used orally at a dosage of 10 to 100 mg/day and by intramuscular injection at a dosage of 300 mg once every 4 weeks. Studies have found that 10, 25, and 50 mg/day CPA in combination with estrogen all result in equivalent and full testosterone suppression in transgender women. In light of risks of CPA such as fatigue, blood clots, benign brain tumors, and liver damage, the use of lower dosages of the medication may help to minimize such risks. The side effects of CPA are more acceptable for transgender women than for cisgender men.
CPA has also been used as a puberty blocker
Puberty blockers, also called puberty inhibitors or hormone blockers, are medicines used to postpone puberty in children. The most commonly used puberty blockers are gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists, which suppress the production ...
and hence as an antiandrogen and antiestrogen to suppress puberty
Puberty is the process of physical changes through which a child's body matures into an adult body capable of sexual reproduction. It is initiated by hormonal signals from the brain to the gonads: the ovaries in a girl, the testes in a ...
in transgender youth
Transgender youth are children or adolescents who do not identify with the sex they were assigned at birth. Because transgender youth are usually dependent on their parents for care, shelter, financial support, and other needs, transgender y ...
, although GnRH modulator
A GnRH modulator, or GnRH receptor modulator, also known as an LHRH modulator or LHRH receptor modulator, is a type of medication which modulates the GnRH receptor, the biological target of the hypothalamic hormone gonadotropin-releasing hormo ...
s are primarily used for this purpose.
Prostate cancer
CPA is used as an antiandrogen monotherapy and means ofandrogen deprivation therapy
Androgen deprivation therapy (ADT), also called androgen suppression therapy, is an antihormone therapy whose main use is in treating prostate cancer. Prostate cancer cells usually require androgen hormones, such as testosterone, to grow. ADT red ...
in the palliative
Palliative care (derived from the Latin root , or 'to cloak') is an interdisciplinary medical caregiving approach aimed at optimizing quality of life and mitigating suffering among people with serious, complex, and often terminal illnesses. Wit ...
treatment of prostate cancer
Prostate cancer is cancer of the prostate. Prostate cancer is the second most common cancerous tumor worldwide and is the fifth leading cause of cancer-related mortality among men. The prostate is a gland in the male reproductive system that su ...
in men. It is used at very high doses by mouth or by intramuscular injection to treat this disease. Antiandrogens do not cure prostate cancer, but can significantly extend life in men with the disease. CPA has similar effectiveness to GnRH modulator
A GnRH modulator, or GnRH receptor modulator, also known as an LHRH modulator or LHRH receptor modulator, is a type of medication which modulates the GnRH receptor, the biological target of the hypothalamic hormone gonadotropin-releasing hormo ...
s and surgical castration, high-dose estrogen
High-dose estrogen (HDE) is a type of hormone therapy in which high doses of estrogens are given. When given in combination with a high dose of a progestogen, it has been referred to as pseudopregnancy. It is called this because the estrogen and p ...
therapy (e.g., with diethylstilbestrol
Diethylstilbestrol (DES), also known as stilbestrol or stilboestrol, is a nonsteroidal estrogen medication, which is presently rarely used. In the past, it was widely used for a variety of indications, including pregnancy support for those with ...
), and high-dose nonsteroidal antiandrogen monotherapy (e.g., with bicalutamide), but has significantly inferior effectiveness to combined androgen blockade Maximum or maximal androgen blockade (MAB) or complete or combined androgen blockade (CAB) is a medical treatment involving the combination of both androgen receptor (AR) antagonism and inhibition or suppression of androgen production to attain ma ...
with a GnRH modulator and a nonsteroidal antiandrogen (e.g., with bicalutamide or enzalutamide). In addition, the combination of CPA with a GnRH modulator or surgical castration has not been found to improve outcomes relative to a GnRH modulator or surgical castration alone, in contrast to nonsteroidal antiandrogens. Due to its inferior effectiveness, tolerability, and safety
Safety is the state of being "safe", the condition of being protected from harm or other danger. Safety can also refer to the control of recognized hazards in order to achieve an acceptable level of risk.
Meanings
There are two slightly di ...
, CPA is rarely used in the treatment of prostate cancer today, having largely been superseded by GnRH modulators and nonsteroidal antiandrogens. CPA is the only steroidal antiandrogen that continues to be used in the treatment of prostate cancer.
Dose-ranging studies of CPA for prostate cancer were not performed, and the optimal dosage of CPA for the treatment of the condition has not been established. A dosage range of oral CPA of 100 to 300 mg/day is used in the treatment of prostate cancer, but generally 150 to 200 mg/day oral CPA is used. Schröder (1993, 2009) reviewed the issue of CPA dosage and recommended a dosage of 200 to 300 mg/day for CPA as a monotherapy and a dosage of 100 to 200 mg/day for CPA in combined androgen blockade Maximum or maximal androgen blockade (MAB) or complete or combined androgen blockade (CAB) is a medical treatment involving the combination of both androgen receptor (AR) antagonism and inhibition or suppression of androgen production to attain ma ...
(that is, CPA in combination with surgical
Surgery ''cheirourgikē'' (composed of χείρ, "hand", and ἔργον, "work"), via la, chirurgiae, meaning "hand work". is a medical specialty that uses operative manual and instrumental techniques on a person to investigate or treat a pat ...
or medical castration
Chemical castration is castration via anaphrodisiac drugs, whether to reduce libido and sexual activity, to treat cancer, or otherwise. Unlike surgical castration, where the gonads are removed through an incision in the body,
). However, the combination of CPA with castration for prostate cancer has been found to significantly decrease overall survival compared to castration alone. Hence, the use CPA as the antiandrogen component in combined androgen blockade would appear not to be advisable. When used by intramuscular injection to treat prostate cancer, CPA is used at a dosage of 300 mg once a week.
The combination of CPA with an estrogen such as ethinylestradiol sulfonate or low-dose diethylstilbestrol
Diethylstilbestrol (DES), also known as stilbestrol or stilboestrol, is a nonsteroidal estrogen medication, which is presently rarely used. In the past, it was widely used for a variety of indications, including pregnancy support for those with ...
has been used as a form of combined androgen blockade and as an alternative to the combination of CPA with surgical or medical castration.
Sexual deviance
CPA is used as an antiandrogen and form ofchemical castration
Chemical castration is castration via anaphrodisiac drugs, whether to reduce libido and sexual activity, to treat cancer, or otherwise. Unlike surgical castration, where the gonads are removed through an incision in the body,
in the treatment of paraphilia
Paraphilia (previously known as sexual perversion and sexual deviation) is the experience of intense sexual arousal to atypical objects, situations, fantasies, behaviors, or individuals. It has also been defined as sexual interest in anything ot ...
s and hypersexuality in men. It is used to treat sex offender
A sex offender (sexual offender, sex abuser, or sexual abuser) is a person who has committed a sex crime. What constitutes a sex crime differs by culture and legal jurisdiction. The majority of convicted sex offenders have convictions for crim ...
s. The medication is approved in more than 20 countries for this indication and is predominantly employed in Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by to ...
, Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
, and the Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabian Peninsula, Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Anatolia, Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Pro ...
. CPA works by decreasing sex drive and sexual arousal
Sexual arousal (also known as sexual excitement) describes the physiological and psychological responses in preparation for sexual intercourse or when exposed to sexual stimuli. A number of physiological responses occur in the body and mind a ...
and producing sexual dysfunction
Sexual dysfunction is difficulty experienced by an individual or partners during any stage of normal sexual activity, including physical pleasure, desire, preference, arousal, or orgasm. The World Health Organization defines sexual dysfunction a ...
. CPA can also be used to reduce sex drive in individuals with inappropriate sexual behaviors, such as people with intellectual disability
Intellectual disability (ID), also known as general learning disability in the United Kingdom and formerly mental retardation, Rosa's Law, Pub. L. 111-256124 Stat. 2643(2010). is a generalized neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by signif ...
and dementia
Dementia is a disorder which manifests as a set of related symptoms, which usually surfaces when the brain is damaged by injury or disease. The symptoms involve progressive impairments in memory, thinking, and behavior, which negatively affe ...
. The medication is also useful for treating self-harmful sexual behavior, such as masochism
Sadomasochism ( ) is the giving and receiving of pleasure from acts involving the receipt or infliction of pain or humiliation. Practitioners of sadomasochism may seek sexual pleasure from their acts. While the terms sadist and masochist refer ...
. CPA has comparable effectiveness to medroxyprogesterone acetate
Medroxyprogesterone acetate (MPA), also known as depot medroxyprogesterone acetate (DMPA) in injectable form and sold under the brand name Depo-Provera among others, is a hormonal medication of the progestin type. It is used as a method of bi ...
in suppressing sexual urges and function but appears to be less effective than GnRH modulator
A GnRH modulator, or GnRH receptor modulator, also known as an LHRH modulator or LHRH receptor modulator, is a type of medication which modulates the GnRH receptor, the biological target of the hypothalamic hormone gonadotropin-releasing hormo ...
s like leuprorelin
Leuprorelin, also known as leuprolide, is a manufactured version of a hormone used to treat prostate cancer, breast cancer, endometriosis, uterine fibroids, as part of transgender hormone therapy, for early puberty, or to perform chemical c ...
and has more side effect
In medicine, a side effect is an effect, whether therapeutic or adverse, that is secondary to the one intended; although the term is predominantly employed to describe adverse effects, it can also apply to beneficial, but unintended, consequence ...
s.
High-dose CPA significantly decreases sexual fantasies
A sexual fantasy or erotic fantasy is a mental image or pattern of thought that stirs a person's sexuality and can create or enhance sexual arousal. A sexual fantasy can be created by the person's imagination or memory, and may be triggered aut ...
and sexual activity in 80 to 90% of men with paraphilias. In addition, it has been found to decrease the rate of reoffending in sex offenders from 85% to 6%, with most of the reoffenses being committed by individuals who did not follow their CPA treatment prescription. It has been reported that in 80% of cases, 100 mg/day CPA is adequate to achieve the desired reduction of sexuality, whereas in the remaining 20% of cases, 200 mg/day is sufficient. When only a partial reduction in sexuality is desired, 50 mg/day CPA can be useful. Reduced sexual desire and erectile function occurs with CPA by the end of the first week of treatment, and becomes maximal within three to four weeks. The dosage range is 50 to 300 mg/day.
Early puberty
CPA is used as an antiandrogen and antiestrogen to treatprecocious puberty
In medicine, precocious puberty is puberty occurring at an unusually early age. In most cases, the process is normal in every aspect except the unusually early age and simply represents a variation of normal development. In a minority of childr ...
in boys and girls. However, it is not fully satisfactory for this indication because it is not able to completely suppress puberty. For this reason, CPA has mostly been superseded by GnRH agonists in the treatment of precocious puberty. CPA is not satisfactory for gonadotropin-independent precocious puberty. CPA has been used at dosages of 50 to 300 mg/m2 to treat precocious puberty.
Other uses
CPA is useful in the treatment ofhot flash
Hot flashes (also known as hot flushes) are a form of flushing, often caused by the changing hormone levels that are characteristic of menopause. They are typically experienced as a feeling of intense heat with sweating and rapid heartbeat, an ...
es, for instance due to androgen deprivation therapy
Androgen deprivation therapy (ADT), also called androgen suppression therapy, is an antihormone therapy whose main use is in treating prostate cancer. Prostate cancer cells usually require androgen hormones, such as testosterone, to grow. ADT red ...
for prostate cancer.
CPA is useful for suppressing the testosterone flare at the initiation of GnRH agonist therapy. It has been used successfully both alone and in combination with estrogen
Estrogen or oestrogen is a category of sex hormone responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics. There are three major endogenous estrogens that have estrogenic hormonal ac ...
s such as diethylstilbestrol
Diethylstilbestrol (DES), also known as stilbestrol or stilboestrol, is a nonsteroidal estrogen medication, which is presently rarely used. In the past, it was widely used for a variety of indications, including pregnancy support for those with ...
for this purpose.
Available forms
CPA is available in the form oforal
The word oral may refer to:
Relating to the mouth
* Relating to the mouth, the first portion of the alimentary canal that primarily receives food and liquid
** Oral administration of medicines
** Oral examination (also known as an oral exam or or ...
tablet
Tablet may refer to:
Medicine
* Tablet (pharmacy), a mixture of pharmacological substances pressed into a small cake or bar, colloquially called a "pill"
Computing
* Tablet computer, a mobile computer that is primarily operated by touching the ...
s alone (higher-dose; 10 mg, 50 mg, 100 mg) or in combination with ethinylestradiol
Ethinylestradiol (EE) is an estrogen medication which is used widely in birth control pills in combination with progestins. In the past, EE was widely used for various indications such as the treatment of menopausal symptoms, gynecological disord ...
or estradiol valerate (low-dose; 1 or 2 mg CPA) and in the form of ampoule
An ampoule (also ampul and ampule) is a small sealed vial which is used to contain and preserve a sample, usually a solid or liquid. Ampoules are usually made of glass.
Modern ampoules are most commonly used to contain pharmaceuticals and chem ...
s for intramuscular injection
Intramuscular injection, often abbreviated IM, is the injection of a substance into a muscle. In medicine, it is one of several methods for parenteral administration of medications. Intramuscular injection may be preferred because muscles hav ...
(higher-dose; 100 mg/mL, 300 mg/3 mL; brand name Androcur Depot).
The higher-dose formulations are used to treat prostate cancer and certain other androgen-related indications while the low-dose formulations which also have an estrogen are used as combined birth control pill
The combined oral contraceptive pill (COCP), often referred to as the birth control pill or colloquially as "the pill", is a type of birth control that is designed to be taken orally by women. The pill contains two important hormones: progesti ...
s and are used in menopausal hormone therapy for the treatment of menopausal symptom
Signs and symptoms are the observed or detectable signs, and experienced symptoms of an illness, injury, or condition. A sign for example may be a higher or lower temperature than normal, raised or lowered blood pressure or an abnormality showi ...
s.
Contraindications
Contraindication
In medicine, a contraindication is a condition that serves as a reason not to take a certain medical treatment due to the harm that it would cause the patient. Contraindication is the opposite of indication, which is a reason to use a certain tre ...
s of CPA include:
* Hypersensitivity
Hypersensitivity (also called hypersensitivity reaction or intolerance) refers to undesirable reactions produced by the normal immune system, including allergies and autoimmunity. They are usually referred to as an over-reaction of the immune ...
to CPA or any of the other components of the medication
* Pregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring develops ( gestates) inside a woman's uterus (womb). A multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Pregnancy usually occurs by sexual intercourse, but ...
, lactation
Lactation describes the secretion of milk from the mammary glands and the period of time that a mother lactates to feed her young. The process naturally occurs with all sexually mature female mammals, although it may predate mammals. The proces ...
, and breastfeeding
Breastfeeding, or nursing, is the process by which human breast milk is fed to a child. Breast milk may be from the breast, or may be expressed by hand or pumped and fed to the infant. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends that bre ...
* Puberty
Puberty is the process of physical changes through which a child's body matures into an adult body capable of sexual reproduction. It is initiated by hormonal signals from the brain to the gonads: the ovaries in a girl, the testes in a ...
(except if being used to treat precocious puberty or delay puberty)
* Liver disease
Liver disease, or hepatic disease, is any of many diseases of the liver. If long-lasting it is termed chronic liver disease. Although the diseases differ in detail, liver diseases often have features in common.
Signs and symptoms
Some of the si ...
s and liver dysfunction
* Chronic kidney disease
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a type of kidney disease in which a gradual loss of kidney function occurs over a period of months to years. Initially generally no symptoms are seen, but later symptoms may include leg swelling, feeling tired, vo ...
* Dubin–Johnson syndrome and Rotor syndrome
* History of jaundice or persistent pruritus during pregnancy
* History of herpes
Herpes simplex is a viral infection caused by the herpes simplex virus. Infections are categorized based on the part of the body infected.
Oral herpes involves the face or mouth. It may result in small blisters in groups often called cold ...
during pregnancy
* Previous or existing liver tumors (only if not due to metastases
Metastasis is a pathogenic agent's spread from an initial or primary site to a different or secondary site within the host's body; the term is typically used when referring to metastasis by a cancerous tumor. The newly pathological sites, the ...
from prostate cancer)
* Previous or existing meningioma
Meningioma, also known as meningeal tumor, is typically a slow-growing tumor that forms from the meninges, the membranous layers surrounding the brain and spinal cord. Symptoms depend on the location and occur as a result of the tumor pressing ...
, hyperprolactinemia, or prolactinoma
* Wasting syndrome
Cachexia () is a complex syndrome associated with an underlying illness, causing ongoing muscle loss that is not entirely reversed with nutritional supplementation. A range of diseases can cause cachexia, most commonly cancer, congestive heart fa ...
s (except in inoperable prostate cancer)
* Severe depression
* Previous or existing thromboembolic processes, as well as stroke
A stroke is a disease, medical condition in which poor cerebral circulation, blood flow to the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: brain ischemia, ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and intracranial hemorrhage, hemorr ...
and myocardial infarction
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow decreases or stops to the coronary artery of the heart, causing damage to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which ma ...
* Severe diabetes
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level ( hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ...
with vascular
The blood vessels are the components of the circulatory system that transport blood throughout the human body. These vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to the tissues of the body. They also take waste and carbon dioxide away f ...
changes
* Sickle-cell anemia
When CPA is used in combination with an estrogen, contraindications for birth control pill
The combined oral contraceptive pill (COCP), often referred to as the birth control pill or colloquially as "the pill", is a type of birth control that is designed to be taken orally by women. The pill contains two important hormones: progesti ...
s should also be considered.
Side effects
CPA is generally well- tolerated and has a mild side-effect profile regardless of dosage when it is used in combination with an estrogen in women. Side effects of CPA in general includehypogonadism
Hypogonadism means diminished functional activity of the gonads—the testes or the ovaries—that may result in diminished production of sex hormones. Low androgen (e.g., testosterone) levels are referred to as hypoandrogenism and low estroge ...
(low sex-hormone levels) and associated symptom
Signs and symptoms are the observed or detectable signs, and experienced symptoms of an illness, injury, or condition. A sign for example may be a higher or lower temperature than normal, raised or lowered blood pressure or an abnormality showi ...
s such as demasculinization
Virilization or masculinization is the biological development of adult male characteristics in young males or females. Most of the changes of virilization are produced by androgens.
Virilization is most commonly used in three medical and biology ...
, sexual dysfunction
Sexual dysfunction is difficulty experienced by an individual or partners during any stage of normal sexual activity, including physical pleasure, desire, preference, arousal, or orgasm. The World Health Organization defines sexual dysfunction a ...
, infertility
Infertility is the inability of a person, animal or plant to reproduce by natural means. It is usually not the natural state of a healthy adult, except notably among certain eusocial species (mostly haplodiploid insects). It is the normal st ...
, and osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a systemic skeletal disorder characterized by low bone mass, micro-architectural deterioration of bone tissue leading to bone fragility, and consequent increase in fracture risk. It is the most common reason for a broken bone a ...
(fragile bones); breast
The breast is one of two prominences located on the upper ventral region of a primate's torso. Both females and males develop breasts from the same embryological tissues.
In females, it serves as the mammary gland, which produces and sec ...
changes such as breast tenderness, breast enlargement, and gynecomastia
Gynecomastia (also spelled gynaecomastia) is the abnormal non-cancerous enlargement of one or both breasts in males due to the growth of breast tissue as a result of a hormone imbalance between estrogens and androgens. Updated by Brent Wisse ( ...
(breasts in men); emotional
Emotions are mental states brought on by neurophysiological changes, variously associated with thoughts, feelings, behavioral responses, and a degree of pleasure or displeasure. There is currently no scientific consensus on a definition ...
changes such as fatigue
Fatigue describes a state of tiredness that does not resolve with rest or sleep. In general usage, fatigue is synonymous with extreme tiredness or exhaustion that normally follows prolonged physical or mental activity. When it does not resolve ...
and depression; and other side effects such as vitamin B12 deficiency
Vitamin B12 deficiency, also known as cobalamin deficiency, is the medical condition in which the blood and tissue have a lower than normal level of vitamin B12. Symptoms can vary from none to severe. Mild deficiency may have few or absent symp ...
, weak glucocorticoid effects, and elevated liver enzymes
In medicine, the presence of elevated transaminases, commonly the transaminases alanine transaminase (ALT) and aspartate transaminase (AST), may be an indicator of liver dysfunction. Other terms include transaminasemia, transaminitis, and elevated ...
. Weight gain
Weight gain is an increase in body weight. This can involve an increase in muscle mass, fat deposits, excess fluids such as water or other factors. Weight gain can be a symptom of a serious medical condition.
Description
Weight gain occurs w ...
can occur with CPA when it is used at high doses. Some of the side effects of CPA can be improved or fully prevented if it is combined with an estrogen to prevent estrogen deficiency. Few quantitative data
Quantitative research is a research strategy that focuses on quantifying the collection and analysis of data. It is formed from a deductive approach where emphasis is placed on the testing of theory, shaped by empiricist and positivist philoso ...
are available on many of the potential side effects of CPA. Pooled tolerability data for CPA is not available in the literature. Cyproterone is also known to suppress andrenocortical function.
At very high doses in aged men with prostate cancer, CPA can cause cardiovascular
The blood circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the entire body of a human or other vertebrate. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, tha ...
side effects. Rarely, CPA can produce blood clot
A thrombus (plural thrombi), colloquially called a blood clot, is the final product of the blood coagulation step in hemostasis. There are two components to a thrombus: aggregated platelets and red blood cells that form a plug, and a mesh of cr ...
s, liver toxicity
Hepatotoxicity (from ''hepatic toxicity'') implies chemical-driven liver damage. Drug-induced liver injury is a cause of acute and chronic liver disease caused specifically by medications and the most common reason for a drug to be withdrawn fr ...
(including hepatitis
Hepatitis is inflammation of the liver tissue. Some people or animals with hepatitis have no symptoms, whereas others develop yellow discoloration of the skin and whites of the eyes ( jaundice), poor appetite, vomiting, tiredness, abdominal ...
, liver failure, and liver cancer
Liver cancer (also known as hepatic cancer, primary hepatic cancer, or primary hepatic malignancy) is cancer that starts in the liver. Liver cancer can be primary (starts in liver) or secondary (meaning cancer which has spread from elsewhere to th ...
), excessively high prolactin levels, and certain benign
Malignancy () is the tendency of a medical condition to become progressively worse.
Malignancy is most familiar as a characterization of cancer. A ''malignant'' tumor contrasts with a non-cancerous ''benign'' tumor in that a malignancy is not s ...
brain tumor
A brain tumor occurs when abnormal cells form within the brain. There are two main types of tumors: malignant tumors and benign (non-cancerous) tumors. These can be further classified as primary tumors, which start within the brain, and seco ...
s including meningioma
Meningioma, also known as meningeal tumor, is typically a slow-growing tumor that forms from the meninges, the membranous layers surrounding the brain and spinal cord. Symptoms depend on the location and occur as a result of the tumor pressing ...
s (tumors of the meninges) and prolactinomas (prolactin
Prolactin (PRL), also known as lactotropin, is a protein best known for its role in enabling mammals to produce milk. It is influential in over 300 separate processes in various vertebrates, including humans. Prolactin is secreted from the pi ...
-secreting tumors of the pituitary gland
In vertebrate anatomy, the pituitary gland, or hypophysis, is an endocrine gland, about the size of a chickpea and weighing, on average, in humans. It is a protrusion off the bottom of the hypothalamus at the base of the brain. The h ...
). Upon discontinuation from high doses, CPA can produce adrenal insufficiency
Adrenal insufficiency is a condition in which the adrenal glands do not produce adequate amounts of steroid hormones. The adrenal gland normally secretes glucocorticoids (primarily cortisol), mineralocorticoids (primarily aldosterone), and andro ...
as a withdrawal effect.
Overdose
CPA is relatively safe in acuteoverdose
A drug overdose (overdose or OD) is the ingestion or application of a drug or other substance in quantities much greater than are recommended.
. It is used at very high doses of up to 300 mg/day by mouth and 700 mg per week by intramuscular injection. For comparison, the dose of CPA used in birth control pills is 2 mg/day. There have been no deaths associated with CPA overdose. There are no specific antidote
An antidote is a substance that can counteract a form of poisoning. The term ultimately derives from the Greek term φάρμακον ἀντίδοτον ''(pharmakon) antidoton'', "(medicine) given as a remedy". Antidotes for anticoagulants are s ...
s for CPA overdose, and treatment should be symptom
Signs and symptoms are the observed or detectable signs, and experienced symptoms of an illness, injury, or condition. A sign for example may be a higher or lower temperature than normal, raised or lowered blood pressure or an abnormality showi ...
-based. Gastric lavage
Gastric lavage, also commonly called stomach pumping or gastric irrigation, is the process of cleaning out the contents of the stomach. Since its first recorded use in early 19th century, it has become one of the most routine means of eliminating p ...
can be used in the event of oral overdose within the last 2 to 3 hours.
Interactions
Inhibitor
Inhibitor or inhibition may refer to:
In biology
* Enzyme inhibitor, a substance that binds to an enzyme and decreases the enzyme's activity
* Reuptake inhibitor, a substance that increases neurotransmission by blocking the reuptake of a neurotra ...
s and inducers of the cytochrome P450
Cytochromes P450 (CYPs) are a superfamily of enzymes containing heme as a cofactor that functions as monooxygenases. In mammals, these proteins oxidize steroids, fatty acids, and xenobiotics, and are important for the clearance of various co ...
enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products ...
CYP3A4
Cytochrome P450 3A4 (abbreviated CYP3A4) () is an important enzyme in the body, mainly found in the liver and in the intestine. It oxidizes small foreign organic molecules ( xenobiotics), such as toxins or drugs, so that they can be removed from ...
may interact
Advocates for Informed Choice, doing business as, dba interACT or interACT Advocates for Intersex Youth, is a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization using innovative strategies to advocate for the legal and human rights of children with intersex trai ...
with CPA. Examples of strong CYP3A4 inhibitors include ketoconazole
Ketoconazole, sold under the brand name Nizoral among others, is an antiandrogen and antifungal medication used to treat a number of fungal infections. Applied to the skin it is used for fungal skin infections such as tinea, cutaneous ca ...
, itraconazole
Itraconazole, sometimes abbreviated ITZ, is an antifungal medication used to treat a number of fungal infections. This includes aspergillosis, blastomycosis, coccidioidomycosis, histoplasmosis, and paracoccidioidomycosis. It may be given by mo ...
, clotrimazole
Clotrimazole, sold under the brand name Lotrimin, among others, is an antifungal medication. It is used to treat vaginal yeast infections, oral thrush, diaper rash, tinea versicolor, and types of ringworm including athlete's foot and jock ...
, and ritonavir
Ritonavir, sold under the brand name Norvir, is an antiretroviral drug used along with other medications to treat HIV/AIDS. This combination treatment is known as highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART). Ritonavir is a protease inhibitor ...
, while examples of strong CYP3A4 inducers include rifampicin
Rifampicin, also known as rifampin, is an ansamycin antibiotic used to treat several types of bacterial infections, including tuberculosis (TB), ''Mycobacterium avium'' complex, leprosy, and Legionnaires’ disease. It is almost always used t ...
, rifampin, phenytoin
Phenytoin (PHT), sold under the brand name Dilantin among others, is an anti-seizure medication. It is useful for the prevention of tonic-clonic seizures (also known as grand mal seizures) and focal seizures, but not absence seizures. The in ...
, carbamazepine
Carbamazepine (CBZ), sold under the trade name Tegretol among others, is an anticonvulsant medication used primarily in the treatment of epilepsy and neuropathic pain. It is used as an adjunctive treatment in schizophrenia along with other m ...
, phenobarbital
Phenobarbital, also known as phenobarbitone or phenobarb, sold under the brand name Luminal among others, is a medication of the barbiturate type. It is recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO) for the treatment of certain types of ep ...
, and St. John's wort. Certain anticonvulsant
Anticonvulsants (also known as antiepileptic drugs or recently as antiseizure drugs) are a diverse group of pharmacological agents used in the treatment of epileptic seizures. Anticonvulsants are also increasingly being used in the treatment of ...
medications can substantially reduce levels of CPA, by as much as 8-fold.
Pharmacology
Pharmacodynamics
CPA hasantiandrogen
Antiandrogens, also known as androgen antagonists or testosterone blockers, are a class of drugs that prevent androgens like testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT) from mediating their biological effects in the body. They act by blocking the ...
ic activity, progestogen
Progestogens, also sometimes written progestagens or gestagens, are a class of natural or synthetic steroid hormones that bind to and activate the progesterone receptors (PR). Progesterone is the major and most important progestogen in the bod ...
ic activity, weak partial
Partial may refer to:
Mathematics
*Partial derivative, derivative with respect to one of several variables of a function, with the other variables held constant
** ∂, a symbol that can denote a partial derivative, sometimes pronounced "partial d ...
glucocorticoid activity, weak steroidogenesis inhibitor activity, and agonist
An agonist is a chemical that activates a receptor to produce a biological response. Receptors are cellular proteins whose activation causes the cell to modify what it is currently doing. In contrast, an antagonist blocks the action of the ag ...
activity at the pregnane X receptor
In the field of molecular biology, the pregnane X receptor (PXR), also known as the steroid and xenobiotic sensing nuclear receptor (SXR) or nuclear receptor subfamily 1, group I, member 2 (NR1I2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ' ...
. It has no estrogen
Estrogen or oestrogen is a category of sex hormone responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics. There are three major endogenous estrogens that have estrogenic hormonal ac ...
ic or antimineralocorticoid
An antimineralocorticoid, also known as a mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist (MRA or MCRA) or aldosterone antagonist, is a diuretic drug which antagonizes the action of aldosterone at mineralocorticoid receptors. This group of drugs is ofte ...
activity. In terms of potency
Potency may refer to:
* Potency (pharmacology), a measure of the activity of a drug in a biological system
* Virility
* Cell potency, a measure of the differentiation potential of stem cells
* In homeopathic dilutions, potency is a measure of how ...
, CPA is described as a highly potent progestogen, a moderately potent antiandrogen, and a weak glucocorticoid. Due to its progestogenic activity, CPA has antigonadotropic
An antigonadotropin is a drug which suppresses the activity and/or downstream effects of one or both of the gonadotropins, follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH). This results in an inhibition of the hypothalamic-pituita ...
effects, and is able to suppress fertility
Fertility is the capability to produce offspring through reproduction following the onset of sexual maturity. The fertility rate is the average number of children born by a female during her lifetime and is quantified demographically. Ferti ...
and sex-hormone levels in both males and females.
Pharmacokinetics
CPA can be takenby mouth
Oral administration is a route of administration where a substance is taken through the mouth. Per os abbreviated to P.O. is sometimes used as a direction for medication to be taken orally. Many medications are taken orally because they are i ...
or by injection into muscle. It has near-complete oral bioavailability
In pharmacology, bioavailability is a subcategory of absorption and is the fraction (%) of an administered drug that reaches the systemic circulation.
By definition, when a medication is administered intravenously, its bioavailability is 100%. Ho ...
, is highly and exclusively bound to albumin
Albumin is a family of globular proteins, the most common of which are the serum albumins. All the proteins of the albumin family are water- soluble, moderately soluble in concentrated salt solutions, and experience heat denaturation. Album ...
in terms of plasma protein binding, is metabolized
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cell ...
in the liver
The liver is a major organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it i ...
by hydroxylation
In chemistry, hydroxylation can refer to:
*(i) most commonly, hydroxylation describes a chemical process that introduces a hydroxyl group () into an organic compound.
*(ii) the ''degree of hydroxylation'' refers to the number of OH groups in a ...
and conjugation
Conjugation or conjugate may refer to:
Linguistics
*Grammatical conjugation, the modification of a verb from its basic form
* Emotive conjugation or Russell's conjugation, the use of loaded language
Mathematics
*Complex conjugation, the change ...
, has 15β-hydroxycyproterone acetate (15β-OH-CPA) as a single major active metabolite An active metabolite is an active form of a drug after it has been processed by the body.
Metabolites of drugs
An active metabolite results when a drug is metabolized by the body into a modified form which continues to produce effects in the body ...
, has a long elimination half-life
Biological half-life (also known as elimination half-life, pharmacologic half-life) is the time taken for concentration of a biological substance (such as a medication) to decrease from its maximum concentration ( Cmax) to half of Cmax in the b ...
of about 2 to 4 days regardless of route of administration, and is excreted in feces
Feces ( or faeces), known colloquially and in slang as poo and poop, are the solid or semi-solid remains of food that was not digested in the small intestine, and has been broken down by bacteria in the large intestine. Feces contain a rela ...
primarily and to a lesser extent in urine
Urine is a liquid by-product of metabolism in humans and in many other animals. Urine flows from the kidneys through the ureters to the urinary bladder. Urination results in urine being excreted from the body through the urethra.
Cellul ...
.
Chemistry
CPA, also known as 1α,2α-methylene-6-chloro-17α-acetoxy-δ6-progesterone or as 1α,2α-methylene-6-chloro-17α-hydroxypregna-4,6-diene-3,20-dione acetate, is asynthetic Synthetic things are composed of multiple parts, often with the implication that they are artificial. In particular, 'synthetic' may refer to:
Science
* Synthetic chemical or compound, produced by the process of chemical synthesis
* Synthetic ...
pregnane steroid
A steroid is a biologically active organic compound with four rings arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes that alter membrane fluidity; and ...
and an acetylated derivative
In mathematics, the derivative of a function of a real variable measures the sensitivity to change of the function value (output value) with respect to a change in its argument (input value). Derivatives are a fundamental tool of calculus. ...
of 17α-hydroxyprogesterone
17α-Hydroxyprogesterone (17α-OHP), also known as 17-OH progesterone (17-OHP), or hydroxyprogesterone (OHP), is an endogenous progestogen steroid hormone related to progesterone. It is also a chemical intermediate in the biosynthesis of many o ...
. It is structurally related to other 17α-hydroxyprogesterone derivatives such as chlormadinone acetate, hydroxyprogesterone caproate, medroxyprogesterone acetate
Medroxyprogesterone acetate (MPA), also known as depot medroxyprogesterone acetate (DMPA) in injectable form and sold under the brand name Depo-Provera among others, is a hormonal medication of the progestin type. It is used as a method of bi ...
, and megestrol acetate.
Synthesis
Chemical syntheses of CPA have been published. The following is one such synthesis: The dehydrogenation of 17α-hydroxyprogesterone acetate 02-23-8(1) with chloranil (tetrachloro-p-benzoquinone) gives a compound that has been called melengestro acetate 25-51-4(2). Dehydrogenation with selenium dioxide gives 17-acetoxy-1,4,6-pregnatriene-3,20-dione 668-75-9(3). Reacting this with diazomethane results in a 1,3-dipolar addition reaction at C1–C2 of the double bond of the steroid system, which forms a derivative of dihydropyrazole
The dehydrogenation of 17α-hydroxyprogesterone acetate 02-23-8(1) with chloranil (tetrachloro-p-benzoquinone) gives a compound that has been called melengestro acetate 25-51-4(2). Dehydrogenation with selenium dioxide gives 17-acetoxy-1,4,6-pregnatriene-3,20-dione 668-75-9(3). Reacting this with diazomethane results in a 1,3-dipolar addition reaction at C1–C2 of the double bond of the steroid system, which forms a derivative of dihydropyrazoleCID:134990386
(4). This compound cleaves when reacted with
perchloric acid
Perchloric acid is a mineral acid with the formula H Cl O4. Usually found as an aqueous solution, this colorless compound is a stronger acid than sulfuric acid, nitric acid and hydrochloric acid. It is a powerful oxidizer when hot, but aqueo ...
,Rudolf Wiechert, (1964). releasing nitrogen molecules and forming a cyclopropane derivative, 6-deschloro cyproterone acetate 701-50-0(5). Selective oxidation of the C6=C7 olefin with benzoyl peroxide gives the epoxide, i.e. 6-deschloro-6,7-epoxy cyproterone 5423-97-9(6). The penultimate step involves a reaction with hydrochloric acid in acetic acid, resulting in the formation of chlorine and its subsequent dehydration, and a simultaneous opening of the cyclopropane ring giving 1α-(chloromethyl) chlormadinone acetate 7183-98-1(7). The heating of this in collidine reforms the cyclopropane ring, completing the synthesis of CPA (8).
History
CPA was first synthesized in 1961 by Rudolf Wiechert, a Schering employee, and together with Friedmund Neumann inBerlin
Berlin ( , ) is the capital and largest city of Germany by both area and population. Its 3.7 million inhabitants make it the European Union's most populous city, according to population within city limits. One of Germany's sixteen constitu ...
, they filed for a patent for CPA as "progestational agent" in 1962. The antiandrogenic activity of CPA was discovered serendipitously by Hamada, Neumann, and Karl Junkmann in 1963. Along with the steroidal antiandrogens benorterone
Benorterone, also known by its developmental code name SKF-7690 and as 17α-methyl-''B''-nortestosterone, is a steroidal antiandrogen which was studied for potential medical use but was never marketed. It was the first known antiandrogen to be s ...
(17α-methyl-''B''-nortestosterone; SKF-7690), cyproterone, BOMT (Ro 7–2340), and trimethyltrienolone (R-2956) and the nonsteroidal antiandrogens flutamide and DIMP (Ro 7–8117), CPA was one of the first antiandrogens to be discovered and researched.
CPA was initially developed as a progestogen for the prevention of threatened abortion
Miscarriage, also known in medical terms as a spontaneous abortion and pregnancy loss, is the death of an embryo or fetus before it is able to survive independently. Miscarriage before 6 weeks of gestation is defined by ESHRE as biochemical lo ...
. As part of its development, it was assessed for androgenic activity to ensure that it would not produce teratogenic effects in female fetus
A fetus or foetus (; plural fetuses, feti, foetuses, or foeti) is the unborn offspring that develops from an animal embryo. Following embryonic development the fetal stage of development takes place. In human prenatal development, fetal dev ...
es. The drug was administered to pregnant
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring develops ( gestates) inside a woman's uterus (womb). A multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Pregnancy usually occurs by sexual intercourse, but ca ...
rats and its effects on the rat fetuses were studied. To the surprise of the researchers, all of the rat pups born appeared to be female. After 20 female rat pups in a row had been counted, it was clear that this could not be a chance occurrence. The rat pups were further evaluated and it was found that, in terms of karyotype
A karyotype is the general appearance of the complete set of metaphase chromosomes in the cells of a species or in an individual organism, mainly including their sizes, numbers, and shapes. Karyotyping is the process by which a karyotype is disce ...
, about 50% were actually males. The male rat pups had been feminized, and this resultant finding constituted the discovery of the powerful antiandrogenic activity of CPA. A year after patent approval in 1965, Neumann published additional evidence of CPA's antiandrogenic effect in rats; he reported an "organizational effect of CPA on the brain". CPA started being used in animal experiments around the world to investigate how antiandrogens affected fetal sexual differentiation
Sexual differentiation is the process of development of the sex differences between males and females from an undifferentiated zygote. Sex determination is often distinct from sex differentiation; sex determination is the designation for the dev ...
.
The first clinical use of CPA in the treatment of sexual deviance and prostate cancer
Prostate cancer is cancer of the prostate. Prostate cancer is the second most common cancerous tumor worldwide and is the fifth leading cause of cancer-related mortality among men. The prostate is a gland in the male reproductive system that su ...
occurred in 1966. It was first studied in the treatment of androgen-dependent skin and hair symptoms, specifically acne, hirsutism, seborrhea, and scalp hair loss, in 1969. CPA was first approved for medical use in 1973 in Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
under the brand name Androcur. In 1977, a formulation of CPA was introduced for use by intramuscular injection. CPA was first marketed as a birth control pill in 1978 in combination with ethinylestradiol under the brand name Diane. Following phase III clinical trial
Clinical trials are prospective biomedical or behavioral research studies on human participants designed to answer specific questions about biomedical or behavioral interventions, including new treatments (such as novel vaccines, drugs, diet ...
s, CPA was approved for the treatment of prostate cancer in Germany in 1980. CPA became available in Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by to ...
as Androcur in 1987, as Androcur Depot in 1990, and as Diane-35 in 1998. Conversely, CPA was never introduced in any form in the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
. This was reportedly due to concerns about breast tumor
A breast mass, also known as a breast lump, is a localized swelling that feel different from the surrounding tissue. Breast pain, nipple discharge, or skin changes may be present. Concerning findings include masses that are hard, do not move ea ...
s observed with high-dose pregnane progestogens in beagle dogs as well as concerns about potential teratogenicity in pregnant women. Use of CPA in transgender women
A trans woman or a transgender woman is a woman who was assigned male at birth. Trans women have a female gender identity, may experience gender dysphoria, and may transition; this process commonly includes hormone replacement therapy and so ...
, an off-label
Off-label use is the use of pharmaceutical drugs for an unapproved indication or in an unapproved age group, dosage, or route of administration. Both prescription drugs and over-the-counter drugs (OTCs) can be used in off-label ways, although ...
indication, was reported as early as 1977. The use of CPA in transgender women was well-established by the early 1990s.
The history of CPA, including its discovery, development, and marketing, has been reviewed.
Society and culture
Generic names
TheEnglish
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ...
and generic name of CPA is ''cyproterone acetate'' and this is its , , and . The English and generic name of unacetylated cyproterone is ''cyproterone'' and this is its and , while ''cyprotérone'' is the and French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
name and ''ciproterone'' is the and Italian name. The name of unesterified cyproterone in Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through ...
is ''cyproteronum'', in German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
is ''cyproteron'', and in Spanish is ''ciproterona''. These names of cyproterone correspond for CPA to ''acétate de cyprotérone'' in French, ''acetato de ciproterona'' in Spanish, ''ciproterone acetato'' in Italian, ''cyproteronacetat'' in German, ''cyproteronacetaat'' in Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
, and ''ciproteron acetat'' in Slavic. CPA is also known by the developmental code names ''SH-80714'' and ''SH-714'', while unacetylated cyproterone is known by the developmental code names ''SH-80881'' and ''SH-881''.
Brand names
CPA is marketed under brand names including Androcur, Androcur Depot, Androcur-100, Androstat, Asoteron, Cyprone, Cyproplex, Cyprostat, Cysaxal, Imvel, and Siterone. When CPA is formulated in combination with ethinylestradiol, it is also known as ''co-cyprindiol'', and brand names for this formulation include Andro-Diane, Bella HEXAL 35, Chloe, Cypretil, Cypretyl, Cyproderm, Diane, Diane Mite, Diane-35, Dianette, Dixi 35, Drina, Elleacnelle, Estelle, Estelle-35, Ginette, Linface, Minerva, Vreya, and Zyrona. CPA is also marketed in combination with estradiol valerate as Climen, Climene, Elamax, and Femilar.Availability
 CPA is widely available throughout the world, and is marketed in almost every developed country, with the notable major exceptions of the
CPA is widely available throughout the world, and is marketed in almost every developed country, with the notable major exceptions of the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
and Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the n ...
.http://www.micromedexsolutions.com/micromedex2/ In almost all countries in which CPA is marketed, it is available both alone and in combination with an estrogen in birth control pills. CPA is marketed widely in combination with both ethinylestradiol
Ethinylestradiol (EE) is an estrogen medication which is used widely in birth control pills in combination with progestins. In the past, EE was widely used for various indications such as the treatment of menopausal symptoms, gynecological disord ...
and estradiol valerate. CPA-containing birth control pills are available in South Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia, constituting the southern part of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and sharing a Korean Demilitarized Zone, land border with North Korea. Its western border is formed ...
, but CPA as a standalone medication is not marketed in this country. In Japan and South Korea, the closely related antiandrogen and progestin chlormadinone acetate, as well as other medications, are used instead of CPA. Specific places in which CPA is marketed include the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and ...
, elsewhere throughout Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
, Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by to ...
, Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands. With an area of , Australia is the largest country by ...
, New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island coun ...
, South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the north by the neighbouring coun ...
, Latin America
Latin America or
* french: Amérique Latine, link=no
* ht, Amerik Latin, link=no
* pt, América Latina, link=no, name=a, sometimes referred to as LatAm is a large cultural region in the Americas where Romance languages — languages derived ...
, and Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an are ...
. CPA is not marketed in most of Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
and the Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabian Peninsula, Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Anatolia, Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Pro ...
.
It has been said that the lack of availability of CPA in the United States explains why there are relatively few studies of it in the treatment of androgen-dependent conditions such as hyperandrogenism and hirsutism in women.
Generation
Progestins in birth control pills are sometimes grouped by generation. While the19-nortestosterone
Nandrolone, also known as 19-nortestosterone, is an androgen and anabolic steroid (AAS) which is used in the form of esters such as nandrolone decanoate (brand name Deca-Durabolin) and nandrolone phenylpropionate (brand name Durabolin). Nandrolon ...
progestins are consistently grouped into generations, the pregnane progestins that are or have been used in birth control pills are typically omitted from such classifications or are grouped simply as "miscellaneous" or "pregnanes". In any case, CPA has been described as a "first-generation" progestin similarly to closely related progestins like chlormadinone acetate, medroxyprogesterone acetate
Medroxyprogesterone acetate (MPA), also known as depot medroxyprogesterone acetate (DMPA) in injectable form and sold under the brand name Depo-Provera among others, is a hormonal medication of the progestin type. It is used as a method of bi ...
, and megestrol acetate.
Research
CPA has been studied and used in combination with low-dosediethylstilbestrol
Diethylstilbestrol (DES), also known as stilbestrol or stilboestrol, is a nonsteroidal estrogen medication, which is presently rarely used. In the past, it was widely used for a variety of indications, including pregnancy support for those with ...
in the treatment of prostate cancer
Prostate cancer is cancer of the prostate. Prostate cancer is the second most common cancerous tumor worldwide and is the fifth leading cause of cancer-related mortality among men. The prostate is a gland in the male reproductive system that su ...
. The combination results in suppression of testosterone levels into the castrate
Castration is any action, surgical, chemical, or otherwise, by which an individual loses use of the testicles: the male gonad. Surgical castration is bilateral orchiectomy (excision of both testicles), while chemical castration uses pharmace ...
range, which normally cannot be achieved with CPA alone. CPA has been studied as a form of androgen deprivation therapy
Androgen deprivation therapy (ADT), also called androgen suppression therapy, is an antihormone therapy whose main use is in treating prostate cancer. Prostate cancer cells usually require androgen hormones, such as testosterone, to grow. ADT red ...
for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), also called prostate enlargement, is a noncancerous increase in size of the prostate gland. Symptoms may include frequent urination, trouble starting to urinate, weak stream, inability to urinate, or loss o ...
(enlarged prostate). The medication has been studied in the treatment of breast cancer
Breast cancer is cancer that develops from breast tissue. Signs of breast cancer may include a lump in the breast, a change in breast shape, dimpling of the skin, milk rejection, fluid coming from the nipple, a newly inverted nipple, or ...
as well.
CPA has been studied for use as a potential male hormonal contraceptive both alone and in combination with testosterone
Testosterone is the primary sex hormone and anabolic steroid in males. In humans, testosterone plays a key role in the development of male reproductive tissues such as testes and prostate, as well as promoting secondary sexual characteristi ...
in men. CPA was under development by Barr Pharmaceuticals in the 2000s for the treatment of hot flash
Hot flashes (also known as hot flushes) are a form of flushing, often caused by the changing hormone levels that are characteristic of menopause. They are typically experienced as a feeling of intense heat with sweating and rapid heartbeat, an ...
es in prostate cancer patients in the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
. It reached phase III clinical trial
Clinical trials are prospective biomedical or behavioral research studies on human participants designed to answer specific questions about biomedical or behavioral interventions, including new treatments (such as novel vaccines, drugs, diet ...
s for this indication and had the tentative brand name CyPat but development was ultimately discontinued in 2008. CPA is not satisfactorily effective as topical
A topical medication is a medication that is applied to a particular place on or in the body. Most often topical medication means application to body surfaces such as the skin or mucous membranes to treat ailments via a large range of classes ...
antiandrogen, for instance in the treatment of acne
Acne, also known as ''acne vulgaris'', is a long-term skin condition that occurs when dead skin cells and oil from the skin clog hair follicles. Typical features of the condition include blackheads or whiteheads, pimples, oily skin, and ...
. CPA has been used to treat estrogen hypersensitivity vulvovaginitis in women.
CPA has been investigated for use in reducing aggression
Aggression is overt or covert, often harmful, social interaction with the intention of inflicting damage or other harm upon another individual; although it can be channeled into creative and practical outlets for some. It may occur either reacti ...
and self-injurious behavior
Self-harm is intentional behavior that is considered harmful to oneself. This is most commonly regarded as direct injury of one's own skin tissues usually without a suicidal intention. Other terms such as cutting, self-injury and self-mutilati ...
via its antiandrogenic effects in conditions like autism spectrum disorder
The autism spectrum, often referred to as just autism or in the context of a professional diagnosis autism spectrum disorder (ASD) or autism spectrum condition (ASC), is a neurodevelopmental condition (or conditions) characterized by difficulti ...
s, dementia
Dementia is a disorder which manifests as a set of related symptoms, which usually surfaces when the brain is damaged by injury or disease. The symptoms involve progressive impairments in memory, thinking, and behavior, which negatively affe ...
s like Alzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease that usually starts slowly and progressively worsens. It is the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in remembering recent events. As ...
, and psychosis
Psychosis is a condition of the mind that results in difficulties determining what is real and what is not real. Symptoms may include delusions and hallucinations, among other features. Additional symptoms are incoherent speech and behavi ...
. CPA may be effective in the treatment of obsessive–compulsive disorder
Obsessive–compulsive disorder (OCD) is a mental and behavioral disorder in which an individual has intrusive thoughts and/or feels the need to perform certain routines repeatedly to the extent where it induces distress or impairs general ...
(OCD). CPA has been studied in the treatment of cluster headache
Cluster headache (CH) is a neurological disorder characterized by recurrent severe headaches on one side of the head, typically around the eye(s). There is often accompanying eye watering, nasal congestion, or swelling around the eye on the af ...
s in men.
See also
*Estradiol valerate/cyproterone acetate
Estradiol valerate/cyproterone acetate (EV/CPA), sold under the brand names Climen and Femilar among others, is a combination product of estradiol valerate (EV), an estrogen, and cyproterone acetate (CPA), a progestogen, which is used in menop ...
* Ethinylestradiol/cyproterone acetate
Ethinylestradiol/cyproterone acetate (EE/CPA), also known as co-cyprindiol and sold under the brand names Diane and Diane-35 among others, is a combination of ethinylestradiol (EE), an estrogen, and cyproterone acetate (CPA), a progestin and ...
References
Further reading
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
/nowiki> - Arznei-Telegramm]
/nowiki>.html" ;"title="/nowiki>Google Translate
/nowiki> {{Navboxes .html" ;"title="/nowiki>Google Translate
/nowiki>">/nowiki>Google Translate
/nowiki> {{Navboxes "> title = Pharmacodynamics , titlestyle = background:#ccccff , list1 = {{Androgen receptor modulators {{Aryl hydrocarbon receptor modulators {{Glucocorticoid receptor modulators {{Opioid receptor modulators {{Progesterone receptor modulators {{Xenobiotic-sensing receptor modulators Cyproterone acetate, 3β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase inhibitors Acetate esters Anti-acne preparations Antiandrogen esters Antigonadotropins Aryl hydrocarbon receptor antagonists Chloroarenes Cyclopropanes CYP17A1 inhibitors Enones Glucocorticoids Hair loss medications Hair removal Hepatotoxins Hormonal antineoplastic drugs Ketones Pregnane X receptor agonists Pregnanes Progestogen esters Progestogens Prolactin releasers Prostate cancer Steroidal antiandrogens